Q&A: Additive Molding for Portable Electronics
Ryan Satcher and Trevor Forward on the ARRIS Applications Engineering Team answer some of the most frequently asked questions about Additive Molding for consumer and industrial electronics.
ARRIS is working with industry-leading brands to level up portable electronics with Additive Molding, an advanced manufacturing technology that aligns high-strength continuous fibers within topology optimized geometries to achieve thinner profiles and better impact resistance for consumer and industrial electronics.
Top 3 Benefits of Additive Molding for Consumer & Industrial Electronics
- Improve drop and impact resistance (achieve much thinner, lighter, more durable form factors)
- Create sleeker devices or more space for larger batteries and other functionality (walls as thin as 0.2mm)
- Incorporate antennae, sensors, wireless charging systems, and other electronic components directly into composite structures

- Ryan Satcher is a Senior Applications Engineer: As a repurposed materials engineer working in product and mechanical design, Ryan has 10+ years of experience working on consumer electronics, medical products, and high-volume manufacturing.
- Trevor Forward is an Applications Engineer: Building on his knowledge in mechanical design, Trevor brings with him experience in consumer electronics, medical devices, and industrial applications.
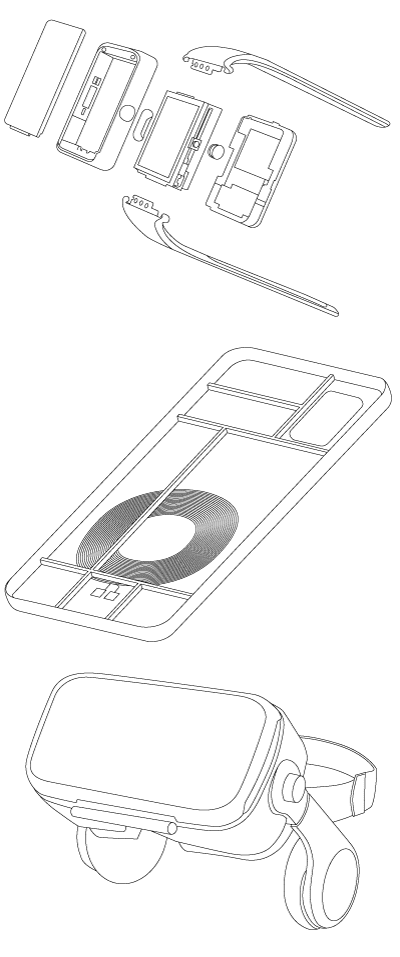
Additive Molding for Portable Electronics
Check out the top eight questions with answers below! Need more information? Contact us directly to schedule a meeting or request a sample part.
How is ARRIS helping companies level up next-gen consumer electronics?
Ryan: ARRIS solves many of today’s most valuable product development problems for engineers and product designers working on consumer and industrial electronic devices. For example, Additive Molding enclosures are made with the highest stiffness- and strength-to-weight materials. Wall thicknesses are also dramatically thinner (READ: “Q&A Ultra-Thin Capabilities“). As a result, parts can be made lighter and tougher than traditional injection-molded parts. Other benefits of Additive Molding include embedded electronics, fiber-reinforced fastener threads, RF transparency with aligned fiber composite materials, etc. The list goes on.
Trevor: Additive Molding is a practical and scalable way of bringing continuous composites with complex geometries to mass-produced electronic devices. I have seen first-hand how this technology and its materials options are helping portable electronics companies reinvent their products in ways not previously possible. These brands are increasing product value for their customers, and these teams are even opening up new product categories to explore further.
What is Additive Molding and why are electronic device companies interested?
Ryan: Additive Molding is an advanced manufacturing technology that enables companies to produce complex product geometries with incredibly high specific stiffness, specific strength, and ultra-thin wall thicknesses at scale. This matters because devices are getting smaller and more compact in the world of IoT. Devices require smaller enclosures and reduced wall thickness for many reasons, and there are physical limitations with injection molding that the industry is now starting to run up against (e.g., wall thickness limit of 0.8mm). Additive Molding is a solution to this challenge by enabling much thinner wall thicknesses made with materials that are also an order of magnitude stiffer and stronger than traditional short chopped fiber plastics.
What types of consumer electronic applications are ideal for Additive Molding?
Ryan: Examples of ideal applications include watch enclosures, phone bezels, camera brackets, AR/VR housings, and other internal structural parts that require a higher level of mechanical performance and RF transparency (READ: “RF Performance of Advanced Composites“).
Trevor: Often, we work with teams on applications where metal parts are replaced with lightweight continuous composites. We also often leverage the ultra-thin capabilities of Additive Molding. Product teams are enabled to create parts too small for traditional injection molding processes while also still achieving the strength and stiffness comparable to metals.
How is ARRIS addressing the wants and needs of consumer electronic product designers and engineers today?
Ryan: Additive Molding provides electronic device product designers with a lot, including a new currency of space, all due to our ability to reduce wall thicknesses. Teams can make a valuable trade, unlocking more performance within the same enclosure volume.
Trevor: To bring next-gen products to markets requires next-gen technologies—ARRIS is one of those next-gen technologies that allow engineers to rethink what’s entirely possible at scale.
Why are ultra-thin parts so critical to consumer electronics and how is ARRIS doing it differently?
Ryan: The only way to make structural parts sub 0.5 mm was with metal that increases weight and blocks RF signal. ARRIS has enabled lightweight, RF-transparent, and structural metal replacement, enabling new form factors and packaging capabilities for handheld and wearable electronics.
Trevor: Ultra-thin parts are a new class of parts altogether. Product development teams can go even smaller than was ever possible using conventional methods without sacrificing strength or stiffness. Less wall thickness means more space for more important things like larger batteries, off-the-shelf antennas, flexes, etc.
What are the mass production capabilities of Additive Molding?
Ryan: Additive Molding delivers 3D-aligned fiber composite parts at high volumes—enabling mass production of high-performance and multi-functional enclosures, housings, bezels, brackets, structures, and more.
Trevor: Unique to Additive Molding, our technology and materials options enable continuous fiber composite parts in complex geometries.. at scale! That’s millions of parts per year. Erick Davidson, our chief engineer (and co-founder), said it best: “ARRIS is very good at aligning fibers within complex parts—we’re the only ones who can do it.”
What are ARRIS customers doing with Additive Molding that you’re most proud of?
Ryan: Our portable electronics customers strive to bring new products to market that historically have not been possible, primarily due to bulk and weight restrictions. These products will change the way we interact with the world, and it’s fun to know that ARRIS is fundamentally enabling better products that will improve the user experience for future generations.
Trevor: Our customers are using Additive Molding exactly how it should be used, and that’s to push beyond the limitations of existing technologies. For example, we helped an electronic device customer increase battery space by nearly 40%. This kind of product development win comes up a lot because using Additive Molding instead of a traditional method allows teams to reduce the thickness and weight of electronic housings by 40-60%. Not only is the part lighter, and there’s more space for larger batteries or new functionality, but the thin-walled continuous carbon fiber part also meets expectations on toughness and durability. For applications where RF transparent materials are required, we can use glass fiber instead of carbon fiber throughout the whole part, or only in specific regions of the part, which can drastically reduce the complexity of integrating components such as antennas and increase connectivity. Teams can genuinely rethink, redesign, and create brand new product categories and experiences that will truly delight their customer base.
What’s next for Additive Molding in the electronics device space?
Trevor: You will just have to wait and see… no, really, watch out for exciting news this year!
Want to meet with Trevor or Ryan to discuss Additive Molding for your product? Start a conversation today, and request to schedule a discovery call with the team—use our contact us page!
Want to join the team and work with experts like Trevor and Ryan? Consider a career at ARRIS at arriscomposites.com/join-us and be part of a fast-growing team that’s transforming how products are imagined, designed, and manufactured.